Scroll pane
With any list, grid or other component that can be scrolled vertically, a scrollbar appears on the right-hand side of the component. The scrollbar is displayed also on pop-up components.
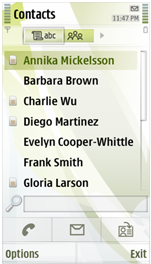
Figure: Scroll pane with scrollbar
The placement of the scroll handle on the scrollbar reflects the position of the focus on the scrolling content.
The size of the scroll handle reflects the number of displayed items relative to the total number of items on the scrolled component.
The scrollbar is displayed even when all items on the component can be displayed in the same view without scrolling. When this is the case, the scroll handle is displayed at the maximum size. The only exception is the Application Shell, where scrollbar is not displayed if all items fit the same view.
Scrollbars in Touch UI
In S60 touch devices, scrollbars (vertical and horizontal) have a touch-enabled scroll box. The hardware keys (Arrow keys) can also be used for scrolling when the scrollbars are visible. The scrolling movement on the screen is smooth.
In order for the scrollbar to be more usable with touch, the actual scrollbar area is wider than the visible scrollbar. When the user scrolls, the scrollbar has a related effect to indicate the scrolling. Because the actual area of scrollbar is wider, the items appearing on that area in scrollable list, grids, viewers etc. cannot be touch-enabled, e.g. list icons in column D cannot be tapped.
Using scrollbars in C++ applications
The API to use for creating the scrollbar component is the Scroller API.
To use a scrollbar in your application, first create a scrollbar
frame using the class CEikScrollbarFrame. All scrollbar operations are executed via this scrollbar frame.
These operations include creating and destroying the scrollbar, setting its
visibility, and adjusting the scrollbar's model. The scrollbar itself can
be created using the method CreateDoubleSpanScrollBarsL() in the class CEikScrollBarFrame.
The class for the scrollbar is CAknDoubleSpanScrollBar. For implementation information, see Creating
a scrollbar.
Scrollbar models encapsulate the range of integers
which a scrollbar can represent, from zero to n, and the current position
of the scrollbar thumb within that range. To set the scrollbar model, use
the class TAknDoubleSpanScrollbarModel. For information on updating the scrollbar's position and size using
the scrollbar model, see Updating
ArrowHead scrollbar attributes and Updating
DoubleSpan scrollbar attributes.
You can control the scrollbar
visibility using the method SetScrollbarVisibilityL() in the class CEikScrollbarFrame.
To observed scrollbar events,
use the class MEikScrollbarObserver. For implementation information, see Observing
scrollbar events.