Design
The MMSMIDlet allows you to create and send MMS messages with text and image content.
The MIDlet UI consists of three screens: one for capturing an image, one for composing the message to be sent, and one for displaying a received message.
To capture an image, select Capture.

Figure: Capturing an image
The message composition screen contains a snapshot of the captured
image and user-editable fields for the destination number and message
text. When you select Send, the MIDlet calls the sendMessage method of the main class and sends the message in a new thread.
Both the receiving and the sending end use the same application ID
in their connections to be able to explicitly communicate with each
other.
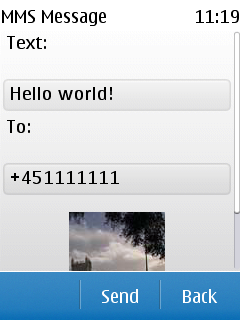
Figure: Composing a message
On the receiving end, the MIDlet listens for incoming messages and displays them upon their arrival. Note that the MIDlet offers no way to manage multiple incoming messages. If it receives several messages in a row, it only displays the last one while the others are lost.
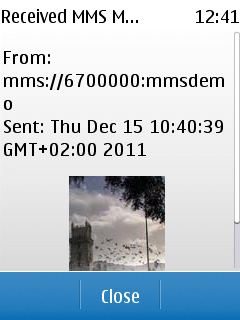
Figure: Receiving a message
Note: In MIDP 2.0, you can use the PushRegistry class to automatically start
a MIDlet when a new message arrives. However, the present MIDlet does
not implement this feature. Because the MIDlet does not register itself
to be woken up when a message arrives, the user on the receiving end
must manually start the MIDlet to process an incoming message. To
test the MIDlet, you can also send messages to its own number.
For instructions on how to implement the MIDlet, see section Implementation.