Installation time security
Authentication
Authorization
Package protection
Authentication
At the authentication phase the authenticity of the application source is checked. This means that both the origin and the integrity of the application must be verifiable.
In authentication the signing certificate and associated certificate
chain, found from the attribute MIDlet-Certificate-<n>-<m> , is validated against one of the root certificates stored in device
memory or SIM card. This is to verify the origin of the application.
After the origin of the application has been verified, the signature
in the attribute MIDlet-Jar-RSA-SHA1 is decrypted
using the verified signing certificate and the public key found from
inside the certificate. The decrypted value is compared to the hash
value calculated at application signing time.
If certificate
attributes ( MIDlet-Certificate-<n>-<m>) are present but signature attribute (MIDlet-Jar-RSA-SHA1) is missing, the application is installed as unidentified.
Following table defines error cases that may be encountered during application authentication and respective error notes:
Error situation |
Symbian user note |
Series 40 user note |
|---|---|---|
If signature attribute ( |
|
|
Any errors in syntax of MIDlet-Jar-RSA-SHA1 and MIDlet-Certificate-<n><m> lead to
installation failure. |
|
|
Validity issues related to root certificates, for example expiration lead to installation failure. |
|
|
If the signature found from JAD does not match with the signature computed over the JAR the installation fails. |
|
|
Trying to update a signed version with an unsigned version of a Java application leads to installation failure. |
|
|
At authentication phase Nokia devices may also check the validity of the certificate online using Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP):
Symbian: The OCSP check is disabled by default. However, there is a user setting in
Application Managerwhich enables the user to turn on the OCSP check. The options for the OCSP check setting are:Must be passed – OCSP check is performed and it must pass in order to install the application.
On – OCSP check is performed but if it fails, it does not necessarily prevent the application installation. Instead, a security warning is shown to the end user, who can choose whether to continue the installation.
Off – Check is not performed.
Series 40: OCSP check is done at the OTA download phase, if the signing certificate has AIA extension. With no AIA extension, the OCSP check is not done. If the check fails, installation fails accordingly with error message
No valid certificate.
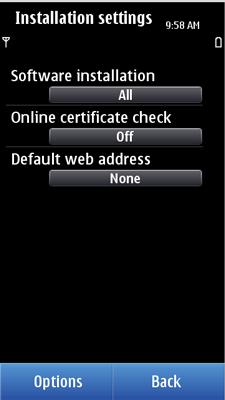
Figure: Symbian OCSP setting
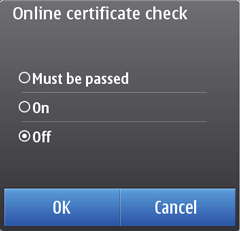
Figure: Online certificate check
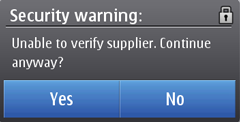
Figure: OCSP check
Errors in Symbian during OCSP check lead to installation
failure with error message Online certificate check failed. Detailed error message can be one of the following:
The revocation state of the certificate used to sign the application could not be determined - if the OCSP state is unknownThe online revocation checking of the certificate used to sign the application could not be conducted. Check your settings.- if the user has not defined the URI to the OCSP responderThe certificate used to sign the application has been revoked either permanently or temporarily (on hold) - if the certificate which signed the application has been revoked
In Symbian devices, the end user defines the URL of the OCSP
responder, against which the check is made. The URL is defined in
the Application Manager setting Default web address.
This setting is used for all the installations but can be overridden
by application's signing certificate (see RFC3280 , chapter 4.2.2.1).
Authorization
At the authorization phase application is bound to the correct
protection domain which is determined based on the root certificate
application was validated against. The protection domain defines which
permissions can be granted to the application and what is the behavior
when application accesses these privileged functions. Signed applications
must explicitly request the permissions using MIDlet-Permissions and MIDlet-Permissions-Opt attributes. Without
requesting the permissions access to those are not granted. The set
of granted permissions represents the intersection between the requested
permissions (collected from both MIDlet-Permissions and MIDlet-Permissions-Opt) and the permissions
available within the protection domain to which the application is
bound to. Failures encountered during the processing of MIDlet-Permissions-Opt
result in ignoring the faulty permission
Following table defines error cases that may be encountered during application authorization and respective error notes:
Error situation |
Symbian user note |
Series 40 user note |
Any failure encountered during the processing of MIDlet-Permissions will fail installation. |
|
|
In Symbian devices, at the installation phase the end user
is provided with an option to configure the application to be security-prompt-free,
which means all the permissions granted to the application are set
as Blanket. This option is presented to the end
user if the application meets the following conditions:
the application is signed
the maximum allowed setting for each of the granted permissions is
Blanket (Always allowed)the default setting of at least one of the requested permissions is something else than
Blanketthe application does not request access to the following two functionalities at the same time:
Application Auto InvocationandNet Access
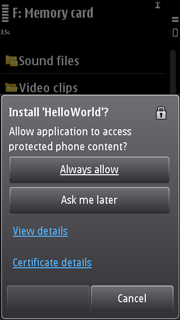
Figure: Setting the application security-prompt free
Package protection
Certain Java packages are protected in the sense that they are reserved by the implementation of the Java Runtime. The protection rule applied means that application classes neither can refer to these packages nor can define classes inside these packages.
In Symbian, violations are checked at installation time and if
violations are found, installation fails with error message Unable to install application. Application authorization failed. Detailed error message is Package<package_name> is protected and can not be used. <package_name> indicates the actual name of the package which is violated by the
application's deployment package.
In Series 40, violations are
checked at runtime and fail with Application Error.