Using video overlays
You can create overlay graphics for video content. You can use video overlays to create, for example, a video player or camera application that displays touch-enabled GUI controls, or a video player that supports subtitles. The video overlays can be opaque or semi-transparent. The following figure shows a video (left) and an overlay (middle) combined into a video with overlay controls (right).
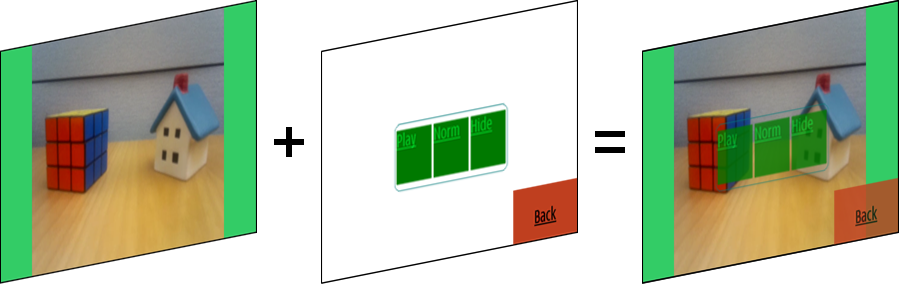
Figure: Combining a video and an overlay
Using video overlays in a MIDlet means rendering 2D graphics over
a video Player. The video player must be displayed on an
LCDUI Canvas (either in normal or full screen mode)
or a Nokia UI API FullCanvas. No other UI components are supported
for rendering video overlays.
To create the overlay graphics for the video player, use the standard graphics APIs. Avoid using M3G content in the video overlays, since 3D graphics consume a lot of memory and can result in poor video playback performance.
Using video overlays is supported on Symbian devices with Java Runtime 2.2 for Symbian or newer.
Video overlays can be used on top of Mobile TV. For more information, see section Mobile broadcasting (DVB-H).
Creating a video overlay
To create a video overlay:
Create a new MIDlet and set it to support video overlays by specifying the
Nokia-UI-EnhancementJAD attribute as follows:Nokia-UI-Enhancement: VideoOverlaySupportedThis attribute value instructs the Java Runtime to render graphics primitives on top of video content if they are drawn with
Canvas.paint. If you do not specify this attribute value, video content is displayed on top of any overlapping graphics drawn with theCanvas.paintmethod, thereby hiding the graphics.In the MIDlet main class, display the UI component that contains the video content and overlay. The following code snippet creates a new
VideoCanvasobject and displays it at MIDlet startup. Displaying theVideoCanvasobject starts a video player and generates a call to theVideoCanvas.paintmethod, which renders the overlay graphics on top of the video player.// display a VideoCanvas when the MIDlet starts public void startApp() { VideoCanvas videoCanvas = new VideoCanvas(); Display.getDisplay(this).setCurrent(videoCanvas); }Implement the UI component on which the video content and overlay are rendered. The following code snippet creates the framework for a custom
Canvasclass calledVideoCanvas.// import the necessary packages and classes import java.io.InputStream; import java.io.IOException; import javax.microedition.lcdui.Canvas; import javax.microedition.lcdui.Graphics; import javax.microedition.media.*; import javax.microedition.media.control.VideoControl; import com.nokia.mid.ui.DirectGraphics; import com.nokia.mid.ui.DirectUtils; public class VideoCanvas extends Canvas { // create a Player and a VideoControl for the video content // ... (see step 4 of this example) // implement the paint() method for rendering the video overlay // ... (see steps 5-8 of this example) } // end class VideoCanvasCreate a
Playerfor the video content, and create aVideoControlfor managing how the video content is displayed. The following code snippet creates aPlayerfor playing back a video file, creates aVideoControlfor thePlayer, and assigns theVideoControltoVideoCanvas.private Player player; private VideoControl videoControl; try { // create a video Player InputStream in = getClass().getResourceAsStream("video.3gp"); player = Manager.createPlayer(in, "video/3gpp"); player.realize(); player.prefetch(); // create a VideoControl for the video Player videoControl = (VideoControl)player.getControl("VideoControl"); // display the video on VideoCanvas and start playback if (videoControl != null) { videoControl.initDisplayMode(VideoControl.USE_DIRECT_VIDEO, this); videoControl.setVisible(true); player.start(); } } catch (IOException e) { } catch (MediaException e) { }To render the video overlay, implement the
Canvas.paintmethod. The following code snippet creates the framework for theVideoCanvas.paintmethod. TheGraphicsparameter is used for rendering the video overlay onVideoCanvas.// render the video overlay by drawing on Graphics g protected void paint(Graphics g) { // store the dimensions of the displayable area of VideoCanvas int displayableWidth = this.getWidth(); int displayableHeight = this.getHeight(); // store the video dimensions int videoWidth = videoControl.getDisplayWidth(); int videoHeight = videoControl.getDisplayHeight(); // store the video position relative to VideoCanvas int videoX = videoControl.getDisplayX(); int videoY = videoControl.getDisplayY(); // clear the video overlay area that lies outside the video area // ... (see step 6 of this example) // optionally, set the video overlay to semi-transparent // ... (see step 7 of this example) // draw the video overlay content // ... (see step 8 of this example) } // end paint()In the
paintmethod, clear the video overlay area that lies outside the video area.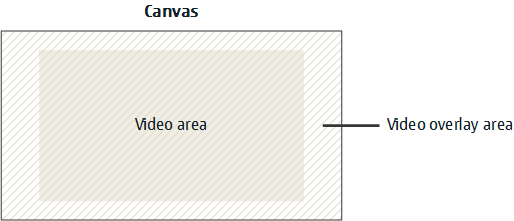
Figure: Video area and video overlay area
The following code snippet uses the
Graphics.fillRectmethod to fill the video overlay area around the video area with black.// set the rendering color for the video overlay to black g.setColor(0); // clear the extra video overlay area by filling it with the rendering color g.fillRect(0, 0, videoX, displayableHeight); g.fillRect(videoX + videoWidth, 0, displayableWidth, displayableHeight); g.fillRect(0, 0, displayableWidth, videoY); g.fillRect(0, videoY + videoHeight, displayableWidth, displayableHeight);
If you want to create a semi-transparent video overlay, specify an alpha channel value for the overlay graphics, or use an image file that already contains an alpha channel. The following code snippet converts the
Graphicsobject of thepaintmethod to aDirectGraphicsobject, and calls theDirectGraphics.setARGBColormethod to set the alpha channel value and rendering color for the video overlay.// set the alpha level (8F) and rendering color (00FFFF) for the video overlay DirectGraphics dg = DirectUtils.getDirectGraphics(g); dg.setARGBColor(0x8F00FFFF);
In the
paintmethod, draw the video overlay content. The following code snippet draws a PNG image on the video overlay by calling theGraphics.drawStringmethod. When theCanvas.paintmethod renders the video overlay, the image is displayed over the video content.// Create an Image InputStream is = getClass().getResourceAsStream("image.png"); Image overlay = Image.createImage(is); // Draw the Image at the center of the video area g.drawImage(overlay, videoX + videoWidth/2, videoY + videoHeight/2, Graphics.VCENTER | Graphics.HCENTER);
Using video overlays correctly
When creating video overlays, note the following:
After you have added the video
Playerand called itsstartmethod, clear the video area by generating an empty paint on theCanvas. To generate an empty paint, call theCanvas.repaintmethod and ensure that it triggers aCanvas.paintoperation where nothing is drawn. This clears any previous content covering the video area. For an example on how to generate an empty paint, see the VideoOverlayMIDlet.To ensure that no portion of the previous screen is shown when the video player is loaded, clear the area outside the video area by calling
Graphics.fillRectfromCanvas.paint. Do not callGraphics.fillRecton the video area, since this hides the video player.To avoid sluggishness during high-quality video playback, do not repaint the
Canvasfrequently.To remove a previously rendered video overlay from the video area, repaint the
Canvasso that nothing is drawn on the video area.You can only render video overlays on
Canvas-based objects. You cannot use video overlays on, for example,GameCanvas,CustomItem,Form Item, or on top of animated GIFs.
Example: VideoOverlayMIDlet
To download a full example MIDlet that shows you how to create video overlays for video playback and for taking pictures with the device camera, click here. The download includes the Eclipse project files for the MIDlet and the JAD and JAR files for installing the MIDlet onto a device.