Verifying a purchase in the back-end server
Using the Purchase Ticket Verification (PTV) API, a back-end server can check with Nokia Store that an in-app purchase was made by a consumer, before delivering the purchased item to the consumer's device.
The verification process is a simple two-way communication:
Back-end server: Sends a
PurchaseVerificationRequestto Nokia Store, identifying the purchased transaction, consumer, and device.Nokia Store: Responds with a
PurchaseVerificationResponseto the back-end server, indicating whether or not the purchase was successful.
For an illustration of the data exchange between a device,back-end server, and Nokia Store, see this purchase flow .
Create an HTTP request
To use the PTV API, you create a script that sends an XML purchase verification request over an HTTPS connection.
The HTTP request contains the following:
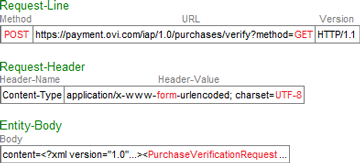
Set these fields:
Method: Set toPOST. Do not useGETfor this field.URL: Set tohttps://payment.ovi.com/iap/1.0/purchases/verify?method=GET. Use theGETmethod here, notPOST.Version: Set to eitherHTTP/1.1orHTTP/1.0.Content-Type: Set toapplication/x-www-form-urlencoded; charset=UTF-8. Theformindicates that theEntity-Bodycontains form data. TheUTF-8identifies the character set being used in the request.Entity-Body: Provide form data consisting of the form parametercontentequated to the XML request. The body must contain characters in the UTF-8 set only.
Create an XML purchase verification request
To verify that an in-app
purchase was successful, your script sends a PurchaseVerificationRequest to Nokia Store. In the request, you can use either of these
XML elements:
PurchaseTicketelement This uses plain text to identify a single purchase transaction, using the XML attributes in the table below.Binaryelement: This is abase64encoding of thePurchaseTicketvalue. This means you must replace characters such as+,/, and=with their corresponding percent-escaped hexadecimal sequences:%2B,%2F, and%3D. You can make the required character replacements through a URL-encoding function call. For example, in Python:body = urllib.urlencode({'content': validationRequest})
When a consumer makes an in-app purchase, Nokia Store processes
the payment and sends a PurchaseCompleted signal
back to the application on the device. The signal includes a base64 encoding of a PurchaseTicket, with all the information in the table below. The application sends
this purchase ticket your script on the back-end server, which can
then independently verify the purchase with Nokia Store before delivering
the purchased item to the device. (See this illustration of the purchase
flow.)
You can use the Binary XML element
to encapsulate the entire PurchaseTicket as-is, without
modification, to send to Nokia Store for verification. If however,
you want to check values within the PurchaseTicket, you can decode the ticket into its components.
The PurchaseTicket element has the following attributes:
Attribute |
Data type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Uniquely identifies the purchase transaction. |
|
|
Identifies the date and time of the purchase. |
|
|
Identifies the type of in-app purchase. Nokia Publish generates
this value when you identify the
in-app purchase items. A device application can also use the in-app purchase
API method |
|
|
Identifies the application. |
|
|
A hashed value of the user's account ID. An application
can also use the in-app purchase API method |
|
|
A hashed value of the user's IMEI. An application can also
use the in-app purchase API method |
|
|
A hashed value of the user's IMSI. An application can also
use the in-app purchase API method |
|
|
Verifies data integrity. The value is a hexadecimal string
presentation of an SHA–1 hash. The hash is calculated over a string
that is derived by concatenating the other |
The PurchaseTicket attributes use the
following data types:
| Data type | Description |
|---|---|
|
A string value, with a length between 1 and 128 characters. |
|
A time in the UTC time zone, for example |
|
A string value, with a length of 128 characters. |
|
A string value, with a length of 40 characters. |
The possible XML elements and attributes as well as their data types are also defined in the PTV API XML schema.
Example of the PurchaseTicket element:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
<PurchaseVerificationRequest xmlns="http://payment.ovi.com/iap">
<PurchaseTicket
transactionId="203491061159"
transactionTime="2011-09-30T22:22:04.000Z"
productId="675193"
applicationId="675199"
accountId="70a956379cf106702bc1704f682fd38775f101d4cfe5c95e66669f4cb3dab20ccb2b0c9c9aa87925aa962ce9710649bd2b42acf4c389967e036f1596c4c8d4da"
imei="da770ec91053e736bc1c4af77551d57a915d7f46ca504df2ca1e06d4246d6102e228694096f809bc664986b93ed0e635c295bd1c9b214947387ba28672a7b6f1"
imsi="da4d9c98a784b9f5f35a4584e68f7a9f01ff993d5256975cfbe209346104fd78cd8e3af072f3d41a490600d5cc4aaf140e3cb82650e3c5756255c296953eabe4"
signature="7bd5cd30576996a90cdac1c61a9f4e43d59242c1"/>
</PurchaseVerificationRequest>
In the example above the signature is calculated as SHA1("2034910611592011-09-30T22:22:04.000Z67519367519970a956379cf106702bc1704f682fd38775f101d4cfe5c95e66669f4cb3dab20ccb2b0c9c9aa87925aa962ce9710649bd2b42acf4c389967e036f1596c4c8d4dada770ec91053e736bc1c4af77551d57a915d7f46ca504df2ca1e06d4246d6102e228694096f809bc664986b93ed0e635c295bd1c9b214947387ba28672a7b6f1").
Note: The signature shown above as well as the Binary element shown below both have long values that might not wrap in
a browser. If the value is truncated, try scrolling the display right
or copying the all text inside the frame to a text editor.
Example of the Binary element:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?> <PurchaseVerificationRequest xmlns="http://payment.ovi.com/iap"> <Binary>PD94bWwgdmVyc2lvbj0iMS4wIiBlbmNvZGluZz0iVVRGLTgiIHN0YW5kYWxvbmU9InllcyI/PjxQdXJjaGFzZVRpY2tldCBzaWduYXR1cmU9IjdiZDVjZDMwNTc2OTk2YTkwY2RhYzFjNjFhOWY0ZTQzZDU5MjQyYzEiIGltc2k9ImRhNGQ5Yzk4YTc4NGI5ZjVmMzVhNDU4NGU2OGY3YTlmMDFmZjk5M2Q1MjU2OTc1Y2ZiZTIwOTM0NjEwNGZkNzhjZDhlM2FmMDcyZjNkNDFhNDkwNjAwZDVjYzRhYWYxNDBlM2NiODI2NTBlM2M1NzU2MjU1YzI5Njk1M2VhYmU0IiBpbWVpPSJkYTc3MGVjOTEwNTNlNzM2YmMxYzRhZjc3NTUxZDU3YTkxNWQ3ZjQ2Y2E1MDRkZjJjYTFlMDZkNDI0NmQ2MTAyZTIyODY5NDA5NmY4MDliYzY2NDk4NmI5M2VkMGU2MzVjMjk1YmQxYzliMjE0OTQ3Mzg3YmEyODY3MmE3YjZmMSIgYWNjb3VudElkPSI3MGE5NTYzNzljZjEwNjcwMmJjMTcwNGY2ODJmZDM4Nzc1ZjEwMWQ0Y2ZlNWM5NWU2NjY2OWY0Y2IzZGFiMjBjY2IyYjBjOWM5YWE4NzkyNWFhOTYyY2U5NzEwNjQ5YmQyYjQyYWNmNGMzODk5NjdlMDM2ZjE1OTZjNGM4ZDRkYSIgcHJvZHVjdElkPSI2NzUxOTMiIGFwcGxpY2F0aW9uSWQ9IjY3NTE5OSIgdHJhbnNhY3Rpb25UaW1lPSIyMDExLTA5LTMwVDIyOjIyOjA0LjAwMFoiIHRyYW5zYWN0aW9uSWQ9IjIwMzQ5MTA2MTE1OSIgeG1sbnM9Imh0dHA6Ly9wYXltZW50Lm92aS5jb20vaWFwIi8+ </Binary> </PurchaseVerificationRequest>
Check the HTTP response status
Nokia Store responds to your HTTP request by sending an HTTP response containing the following:
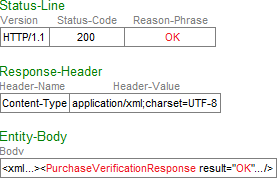
Status-Line, a Status-Code indicates the result of the HTTP request, using standard HTTP codes:200: The HTTP request succeeded. For Purchase Ticket Verifications, theEntity-Bodycontains an XML response document.- A status code other than
200: The HTTP request failed. TheReason-Phrasedescribes the error. An error you might encounter is400 Bad Request, which can indicate one of the following types of HTTP syntax errors:Invalid HTTP method, for example, using
GETinstead ofPOSTin the HTTP Request-Line Method field.Invalid character that is not in the UTF-8 character set, for example, using curly quotes (also called smart quotes) “ ” instead of straight quotes " " to enclose an XML attribute value
Missing
content=in theEntity-Bodyof the HTTP requestAdding a
content=where it is not required, in theEntity-Bodyof the HTTP response
Check the purchase verification response
If the HTTP Status-Code is OK, the Entity-Body contains an XML PurchaseVerificationResponse element with a result attribute indicating the result of the specified in-app purchase
transaction:
Value |
Description |
|---|---|
|
The payment succeeded. |
|
The payment failed. |
|
The payment was refunded. |
|
The |
Example of a purchase verification response:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?> <PurchaseVerificationResponse result="OK" xmlns="http://payment.ovi.com/iap"/>
Sample script
For a complete PHP script showing how to encode both
a PurchaseVerificationRequest, see the server-side
script ptvManager.php for the BuyAndDownloadExample.