Appendix B: Supported root certificates
A root certificate identifies the Root Certificate Authority and is used to “sign” other certificates issued by the CA.
Following table shows the root certificates supported by Nokia Symbian and Series 40 devices and how they are mapped to protection domains.
Devices can include also other root certificates for Java application signing, for example root certificates provided by operators.Symbian devices
The root certificates applicable
to Java can be viewed and managed from Settings —> Phone
—> Phone mgmt. —> General —> Security settings —> Certificate management
—> Authority certificates; they are prefixed with Java
Trust Root.
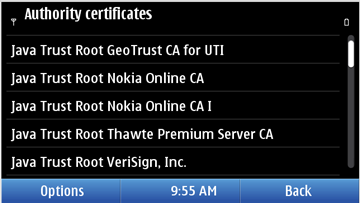
Figure: Root certificate path
UTI, assigned to Identified 3rd Party domain
Thawte, assigned to Identified 3rd Party domain
Verisign, assigned to Identified 3rd Party domain
Nokia, assigned to Manufacturer domain
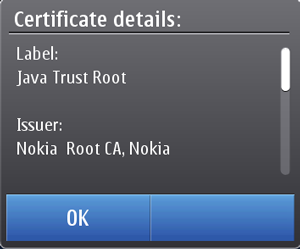
Figure: Nokia root
Identified 3rd Party. As a consequence, Java applications
signed with disabled/deleted roots can not be installed (see screenshot
of a result of such installation). 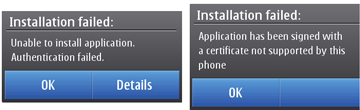
Figure: Installation failure
Already installed Java applications signed with a root which is disabled can not be started until the root is re-enabled (see screenshot)
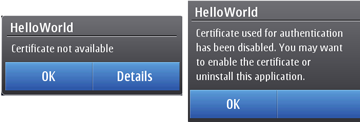
Figure: Disabled root
Already installed Java applications signed with a root which is deleted can not be started anymore (see screenshot)
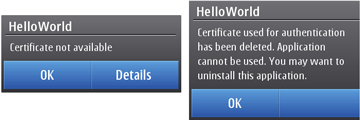
Figure: Deleted root