Example: Handling audio, image, and text content
This example MIDlet suite shows you how to use the Content Handler API on Series 40 devices to:
Handle content locally in a MIDlet
Invoke content in an external content handling application
Register an application as a content handler
This example also shows you how to define the correct JAD attributes for content handling.
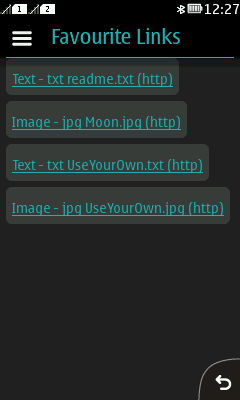
Figure: ContentHandler MIDlet suite
Note: From Java Runtime 2.3 for Symbian onwards, the Symbian platform provides limited support for the Content Handler API: it is possible to pass content from a MIDlet to a native content handler, that is, a native Symbian application. MIDlets cannot themselves function as content handlers. In the present example, therefore, invoking the native content handler for an image file is the only part of the MIDlet suite that would work on a Symbian device. The audio and text handling functions do not work, since it is currently not possible for a Symbian MIDlet to receive content from itself, another MIDlet, or a native application.
Prerequisites
You need the following to develop and test this MIDlet:
Series 40 5th Edition FP1 SDK or newer
Series 40 5th Edition FP1 device or newer
You also need to set up the resources on an Internet server from where the MIDlet can download them. When you test the MIDlet in an emulator, you may need to configure your firewall or Internet settings to allow access to the server. Another option is to use your local workstation as a web server, for example by using Apache HTTP Server, and load the resources from there.
For instructions on how to set up the Java ME development environment, see section Setting up the development environment.
Development
For more information about the MIDlet, see:
Design for information about the design and functionality of the MIDlet
Implementation for information about implementing the MIDlet
You can download the project files for the MIDlet from the download page.