Introduction to Java ME
The Java™ platform is available in three different editions, each optimised for a specific application environment:
Java Platform, Standard Edition (Java SE)
Java Platform, Enterprise Edition (Java EE)
Java Platform, Micro Edition (Java ME)
The three editions are similar in their fundamental aspects and share the common Java characteristics, such as automatic garbage collection and cross-platform virtual machine architecture.
Java ME offers a standard framework for developing Java applications for mobile and other embedded devices, such as mobile phones, and is optimised for an application environment with limited memory and computing resources. Java ME shares a number of APIs with Java SE and Java EE, so you can easily adapt your Java programming skills to create mobile Java applications.
To run Java ME applications, devices must implement a configuration. Configurations specify the minimum set of Java APIs and virtual machine features required to implement a Java ME runtime environment. Java ME defines two configurations:
Connected Device Configuration (CDC)
Connected Limited Device Configuration (CLDC)
To provide developers a full platform for creating Java ME applications, devices must also implement a profile. Profiles sit on top of configurations and specify further Java APIs that focus on specific groups of devices. Mobile devices use the Mobile Information Device Profile (MIDP) on top of CLDC. MIDP adds Java APIs specific to resource-constrained devices such as cell phones. Any device that implements a CLDC configuration and a MIDP profile can run Java ME applications developed for any other device with a corresponding implementation. Java ME applications that use MIDP are called MIDlets.
In addition to the mandatory CLDC configuration and MIDP profile, mobile devices can support additional APIs for more specific purposes, such as drawing vector graphics, using advanced multimedia features, or accessing web services.
The following figure provides an overview of the different Java platforms editions.
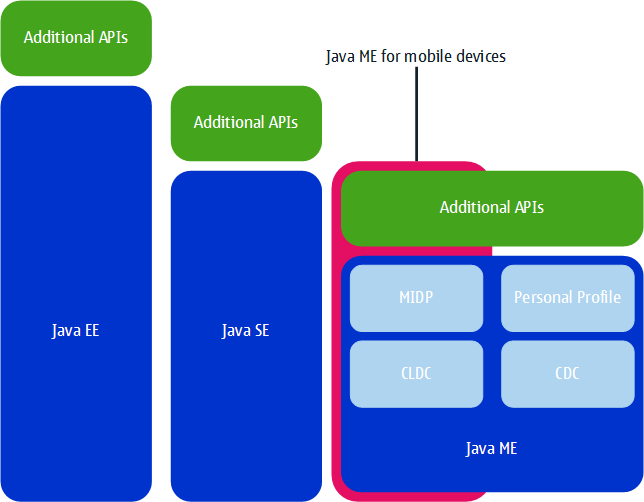
Figure: Java platform editions
The Java ME enabled devices of Nokia support MIDP on top of CLDC.
The Nokia
Asha software platform and Series 40 platforms have supported Java™ ME since their first release, Series 40 1st
Edition. Series 40 2nd Edition was the first release to support the JSR-185
Java Technology for the Wireless Industry (JTWI) specification,
which defines an architecture for a uniform implementation of Java
ME across mobile devices. JTWI was superseded by support for the JSR-248
Mobile Service Architecture (MSA) Subset specification from
Series 40 5th Edition onwards. Like JTWI, MSA aims to minimize the
fragmentation of Java ME implementations and thereby ensure application
compatibility and portability across the broadest possible range of
mobile devices. In Nokia Asha software platform devices, the JSR-248
MSA Subset is supported except for the JSR-75 PIM ToDoList functionality due to lack of native support. For more information
about these two architecture specifications, see:
Java Technology for the Wireless Industry (JTWI) at the Oracle Sun Developer Network
The Mobile Service Architecture Specification at the Oracle Sun Developer Network
Java ME Technology at the Oracle Technology Network
In addition to the mandatory CLDC and MIDP implementations, the Series 40 platforms support a number of additional Java APIs for more specific purposes. The following figure summarizes the common APIs supported by both platforms as well as APIs exclusive to a platform. For detailed information about the APIs, including which API version is supported in which platform release, and which APIs are not supported on Series 40 Lite platforms, see section Supported JAVA APIs.