TextBox
TextBox is a text editor that takes up the whole main pane, operating effectively in full screen mode. Contents are automatically wrapped around from one row to the next.
A TextBox can have input constraints, such as PASSWORD, which obscures the actual characters that are being typed.
A TextBox turns automatically active, when it becomes the foreground Displayable or when it resumes input focus. TextBox supports copy and paste functionality.
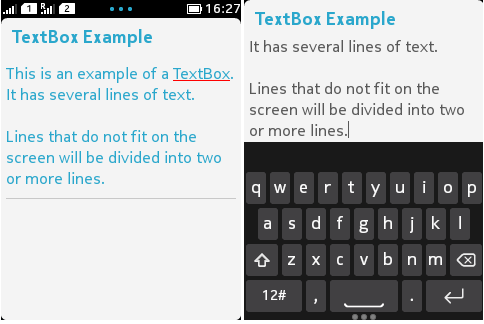
Figure: Example of a full screen TextBox
Source codes for the example:
MIDlet source code
import javax.microedition.midlet.*;
import javax.microedition.lcdui.*;
public class ExampleTextbox extends MIDlet {
Display display = Display.getDisplay(this);
public void startApp() [curly bracket {]
// TextBox(title, text, size, contrains)
TextBox textbox = new TextBox("TextBox Example", "This is an example of a TextBox.\n"
+"It has several lines of text.\n"
+"\n"
+"Lines that do not fit on the screen will be divided into two or more lines.", 255, 0);
display.setCurrent(textbox);
}
public void pauseApp() {
}
public void destroyApp(boolean unconditional) {
}
}
TextBox and TextField with input constraint TextField.ANY support input of the set of characters as specified by item 42 in the Change Log Section on Page 9 of the JSR 118 specifications.
TextBox and TextField have an upper limit on the maximum number of characters that can be stored in them. For the Series 40 platform this is set to 5000 characters.
Additional operations such as text selecting, text copying and pasting are not available in Nokia Asha or Series 40 software platform devices.
-
Touch down and release on an editable TextBox activates the field for editing.
-
Touch down and release within the selected TextBox moves the text cursor to the point of the tap, provided that there is some text on that point. If there is no text and the user taps the empty space of the TextBox the cursor moves to the end of the text.
-
On Series 40 touch and type devices, text can be edited by using the physical keypad. On Nokia Asha and Series 40 full touch software platform devices, text can be edited by using the VirtualKeyboard.
-
The VirtualKeyboard is displayed by default, when the TextBox instance becomes the current Displayable on Nokia Asha software platform devices. On Series 40 full touch devices, the VirtualKeyboard becomes visible, only after the user has tapped inside the TextBox area.
On Series 40 touch and type devices, the scrollbar of a TextBox is always visible, unlike Nokia Asha and Series 40 full touch software platform devices, where the scrollbar is self-dismissible.
Keyboard support
The support for a full keyboard in TextBoxes works in the same way as that of text input in native editors. Note, however, that some of the text constraints are meaningless in full keyboard editors:
-
Full keyboard editors do not always have automatic casing functionality so, for example, INITIAL_CAPS_WORD and INITIAL_CAPS_SENTENCE are ignored in them.
-
Since predictive text input (T9) is always turned off (or completely unavailable) in full keyboard input, the NON_PREDICTIVE mode does not have any effect on the editor.
-
In devices that allow swapping from full keyboard mode to numeric keypad and vice versa, these constraints work as expected in numeric keypad mode.
Constraints and modifiers
The following tables present the different possible TextBox modifiers and constraints.
|
TextBox modifier |
Basic editing style |
|---|---|
|
ANY |
Normal, unconstrained editing.
|
|
URL or EMAILADDR |
Alpha Editing in special URL / e-mail address entry mode.
|
|
PHONENUMBER |
Phone number entry (standard number mode).
|
|
NUMERIC |
Basic number editing:
|
|
DECIMAL |
As defined in MIDP 2.1 API specification. Only a decimal separator (period "." or comma “,”),the minus sign "-", and the decimal digits are allowed in the application-visible text property of TextBox/TextField; i.e. when passed to TextField or TextBox programmatically or returned to the application. |
|
Input constraint modifier |
Supported with Input Constraints |
Description of modifier |
|---|---|---|
|
PASSWORD |
All |
Text entered into TextBox/TextField is confidential data that is obscured.
|
|
UNEDITABLE |
All |
The contents of TextBox/TextField are not user-editable, but the cursor is visible. When user tries to edit the text, normal key press tone is generated. Editing space indicator is not shown. |
|
INITIAL_CAPS_SENTENCE |
ANY, but not with ANY | PASSWORD. |
The modifier sets the editor’s initial case mode to text case. The user is allowed to change the mode. If predictive text input method is supported in the implementation, it is possible to use it also in an INITIAL_CAPS_SENTENCE type editor. If the current input language does not have the concept of capitals, this modifier is simply ignored. The modifier is used if the input mode changes to a language with capital letters. |
|
INITIAL_CAPS_WORD |
None. This is not supported. If the user tries to set this modifier, the attempt is ignored. |
The modifier sets the editor’s initial case mode to title case. |
|
NON_PREDICTIVE or SENSITIVE |
ANY |
Disables predictive text input method. |
Initial input modes
MIDlet can set the initial input mode by calling the setInitialInputMode(String characterSubset) method.
-
The parameter characterSubset is a character subset specifier string, which can be a Unicode character block name (java.lang.Character.UnicodeBlock), an input subset as defined by the Java SE class java.awt.im.InputSubset, or a MIDP-defined subset.
|
Editor (native) properties |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
|
MIDP input mode |
Local input language |
Input mode |
Casing |
|
IS_LATIN |
If the common input language or the display language in the device is a Latin language, that language is used as the local input language, otherwise English is used. |
Latin text input mode; in Japanese, half width Latin mode |
Text case |
|
IS_LATIN_DIGITS |
Input language is not changed. |
Number input mode |
- |
|
MIDP_UPPERCASE_LATIN |
See IS_LATIN |
See IS_LATIN |
Upper case |
|
MIDP_LOWERCASE_LATIN |
See IS_LATIN |
See IS_LATIN |
Lower case |
|
UCB_BASIC_LATIN |
See IS_LATIN |
See IS_LATIN |
Text case |
|
UCB_GREEK |
Greek |
Text input mode |
Text case |
|
UCB_CYRILLIC |
If the common input language or the display language in the device is a Cyrillic language, that language is used as the local input language, otherwise Russian is used. |
Text input mode |
Text case |
|
UCB_HEBREW |
Hebrew |
Text input mode |
- |
|
UCB_ARABIC |
If the common input language or the display language in the device is an Arabic language, that language is used as the local input language, otherwise Arabic is used. |
Text input mode |
- |
|
UCB_THAI |
Thai |
Text input mode |
- |
|
UCB_HIRAGANA |
Japanese |
Hiragana/kanji input mode |
- |
|
UCB_KATAKANA |
Japanese |
Katakana input mode, full width |
- |
|
IS_HALFWIDTH_KATAKANA |
Japanese |
Katakana input mode, half width |
- |
|
IS_KANJI |
Japanese |
Hiragana/kanji input mode |
- |
|
IS_FULLWIDTH_DIGITS |
Japanese |
Number input mode, full width |
- |
|
IS_FULLWIDTH_LATIN |
Japanese |
Latin input mode, full width |
Text case |
|
IS_SIMPLIFIED_HANZI |
Chinese Simplified (Peoples Republic of China) |
The default input method, which normally is Pinyin but the user may have changed it in General Settings. |
- |
|
IS_TRADITIONAL_HANZI |
If the common input language or the display language in the device is a Traditional Hanzi language, that language is used as the local input language, otherwise the local input language is not changed. |
The default input method, which normally is Stroke for Hong Kong and Zhuyin for Taiwan but the user may have changed it in General Settings. |
- |
Automatic character casing modes (such as text case) are not used with constraints EMAILADDR, URL or PASSWORD, although mentioned in the above table.
For information on TextBox implementation in Touch UI -enabled devices, see section Displayables and Commands .
For more information about TextBox see: