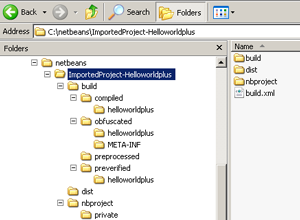
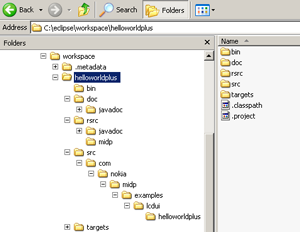
MIDP project structure
This phase describes the structure of a working environment for the project. On default settings, Eclipse and NetBeans use slightly different directory names, but divide the content in the same way as described below. This section deals with the issue based on a development environment that includes Eclipse and S60 MIDP SDK.
The following images show the folder structure in Eclipse and NetBeans.
The content of the folders can be divided in several categories:
Source files
The MIDlet source code is written in these plain text files using an IDE or a text editor. They are also known as Java files and use extension
*.java. These are commonly located in thesrcfolder.Compiled class files
Java class files (
*.class) are source files compiled into bytecode format so that they can be interpreted and executed by the Java Virtual Machine (JVM). During the compilation process these files are also preverified for mobile environment compatibility. Eclipse places Java class files in thebinfolder and NetBeans places them in thebuildfolder.Resource files
Resource files are optional media files that can include icons or image, audio, video and document files that need to be enclosed with the MIDlet and are required by the application. Resource files are located in the
resfolder. S60 platform supports most common media types such as MP3, WMA, MP4, JPEG, PNG, WAV, RM, and others. For a full list of supported formats on different mobile devices, see Multimedia page at Forum Nokia web site.Deployed packages
After the build process has been completed successfully, the class files are collected in a JAR file that is used to distribute the MIDlet to mobile devices. These packages are placed in
deployedfolder when using Eclipse anddistfolder when using NetBeans.