Security risks in the MIDP environment
This section introduces the security threats in the mobile environment and some of the targets of those threats.
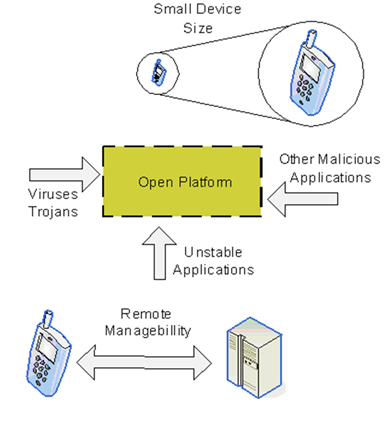
The following figure illustrates some of the threats to mobile devices:
The main security threats in the mobile environment are:
Loss or theft of devices – mobile devices (or their removable media, otherwise known as memory cards) are quite small and are carried by their users. Therefore, they can be easily lost or stolen.
Viruses, Trojans, or unstable or other malicious applications – mobile devices allow 3rd party applications to be installed, to access device capabilities and to be used by other, possibly 3rd party, applications. Therefore, devices are now exposed to the threats associated with the installation of applications of unknown origin in a more open environment.
Misuse of remote management – mobile devices allow applications to be delivered, deployed, operated, and maintained remotely by management servers, possibly without the knowledge or consent of the device user. This remote management therefore poses a security threat to these devices.
The possible targets of these security threats include:
Personal data stored on the mobile device. This includes access information for internet banking, credit card numbers, building access codes, or family related information.
Business data stored on the mobile device. This includes client contact information, project launches, marketing plans, or product specifications.
Business infrastructure accessed by the mobile device. This includes file storage systems, accounting systems, e-mail systems, or security systems.
Device operating system. This includes access to the device file system, access to other applications or access to management capabilities. Note that erroneous or malicious applications can cause damage to these areas.
As a part of regular use, applications on a device may need to communicate with the device user in security related questions. The operating system may need to ask the user to enter a password or PIN, an application installer may prompt the user to confirm the installation of some software, a secure file system implementation may prompt for a password. Malicious applications may try to masquerade as trusted applications and obtain sensitive information by misleading the user.