Name
The Main Event Loop — manages all available sources of events.
Library
glib.lib
Synopsis
#include <glib.h>
GMainLoop;
GMainLoop* g_main_loop_new (GMainContext *context, gboolean is_running);
GMainLoop* g_main_loop_ref (GMainLoop *loop);
void g_main_loop_unref (GMainLoop *loop);
void g_main_loop_run (GMainLoop *loop);
void g_main_loop_quit (GMainLoop *loop);
gboolean g_main_loop_is_running (GMainLoop *loop);
GMainContext* g_main_loop_get_context (GMainLoop *loop);
#define g_main_new (is_running)
#define g_main_destroy (loop)
#define g_main_run (loop)
#define g_main_quit (loop)
#define g_main_is_running (loop)
#define G_PRIORITY_HIGH
#define G_PRIORITY_DEFAULT
#define G_PRIORITY_HIGH_IDLE
#define G_PRIORITY_DEFAULT_IDLE
#define G_PRIORITY_LOW
GMainContext;
GMainContext* g_main_context_new (void);
GMainContext* g_main_context_ref (GMainContext *context);
void g_main_context_unref (GMainContext *context);
GMainContext* g_main_context_default (void);
gboolean g_main_context_iteration (GMainContext *context, gboolean may_block);
#define g_main_iteration (may_block)
gboolean g_main_context_pending (GMainContext *context);
#define g_main_pending ()
GSource* g_main_context_find_source_by_id (GMainContext *context, guint source_id);
GSource* g_main_context_find_source_by_user_data (GMainContext *context, gpointer user_data);
GSource* g_main_context_find_source_by_funcs_user_data (GMainContext *context, GSourceFuncs *funcs, gpointer user_data);
void g_main_context_wakeup (GMainContext *context);
gboolean g_main_context_acquire (GMainContext *context);
void g_main_context_release (GMainContext *context); gboolean g_main_context_is_owner (GMainContext *context);
gboolean g_main_context_wait (GMainContext *context, GCond *cond, GMutex *mutex);
gboolean g_main_context_prepare (GMainContext *context, gint *priority);
gint g_main_context_query (GMainContext *context, gint max_priority, gint *timeout_, GPollFD *fds, gint n_fds);
gint g_main_context_check (GMainContext *context, gint max_priority, GPollFD *fds, gint n_fds);
void g_main_context_dispatch (GMainContext *context);
void g_main_context_set_poll_func (GMainContext *context, GPollFunc func);
GPollFunc g_main_context_get_poll_func (GMainContext *context);
gint (*GPollFunc) (GPollFD *ufds, guint nfsd, gint timeout_);
void g_main_context_add_poll (GMainContext *context, GPollFD *fd, gint priority);
void g_main_context_remove_poll (GMainContext *context, GPollFD *fd);
int g_main_depth (void);
#define g_main_set_poll_func (func)
GSource* g_timeout_source_new (guint interval);
guint g_timeout_add (guint interval, GSourceFunc function, gpointer data);
guint g_timeout_add_full (gint priority, guint interval, GSourceFunc function, gpointer data, GDestroyNotify notify);
GSource* g_idle_source_new (void);
guint g_idle_add (GSourceFunc function, gpointer data);
guint g_idle_add_full (gint priority, GSourceFunc function, gpointer data, GDestroyNotify notify);
gboolean g_idle_remove_by_data (gpointer data);
typedef GPid;
void (*GChildWatchFunc) (GPid pid, gint status, gpointer data);
GSource* g_child_watch_source_new (GPid pid);
guint g_child_watch_add (GPid pid, GChildWatchFunc function, gpointer data);
guint g_child_watch_add_full (gint priority, GPid pid, GChildWatchFunc function, gpointer data, GDestroyNotify notify);
GPollFD;
GSource;
void (*GSourceDummyMarshal) (void);
GSourceFuncs;
GSourceCallbackFuncs;
GSource* g_source_new (GSourceFuncs *source_funcs, guint struct_size);
GSource* g_source_ref (GSource *source);
void g_source_unref (GSource *source);
guint g_source_attach (GSource *source, GMainContext *context);
void g_source_destroy (GSource *source);
void g_source_set_priority (GSource *source, gint priority);
gint g_source_get_priority (GSource *source);
void g_source_set_can_recurse (GSource *source, gboolean can_recurse);
gboolean g_source_get_can_recurse (GSource *source);
guint g_source_get_id (GSource *source);
GMainContext* g_source_get_context (GSource *source);
void g_source_set_callback (GSource *source, GSourceFunc func, gpointer data, GDestroyNotify notify);
gboolean (*GSourceFunc) (gpointer data);
void g_source_set_callback_indirect (GSource *source, gpointer callback_data, GSourceCallbackFuncs *callback_funcs);
void g_source_add_poll (GSource *source, GPollFD *fd);
void g_source_remove_poll (GSource *source, GPollFD *fd);
void g_source_get_current_time (GSource *source, GTimeVal *timeval);
gboolean g_source_remove (guint tag);
gboolean g_source_remove_by_funcs_user_data (GSourceFuncs *funcs, gpointer user_data);
gboolean g_source_remove_by_user_data (gpointer user_data);
Detailed Description
The main event loop manages all the available sources of events for GLib and
GTK+ applications. These events can come from any number of different types of
sources such as file descriptors (plain files, pipes or sockets) and timeouts.
New types of event sources can also be added using g_source_attach().
To allow multiple independent sets of sources to be handled in different threads, each source is associated with a GMainContext. A GMainContext can only be running in a single thread, but sources can be added to it and removed from it from other threads.
Each event source is assigned a priority. The default priority, G_PRIORITY_DEFAULT, is 0. Values less than 0 denote higher priorities. Values greater than 0 denote lower priorities. Events from high priority sources are always processed before events from lower priority sources.
Idle functions can also be added, and assigned a priority. These will be run whenever no events with a higher priority are ready to be processed.
The GMainLoop data type represents a main event loop. A GMainLoop is created with g_main_loop_new(). After adding the initial event
sources, g_main_loop_run() is called. This continuously
checks for new events from each of the event sources and dispatches them.
Finally, the processing of an event from one of the sources leads to a call to g_main_loop_quit() to exit the main loop, and g_main_loop_run() returns.
It is possible to create new instances of GMainLoop recursively. This is often used in GTK+ applications when showing modal dialog boxes. Note that event sources are associated with a particular GMainContext, and will be checked and dispatched for all main loops associated with that GMainContext.
GTK+ contains wrappers of some of these functions, e.g.
gtk_main(),
gtk_main_quit()
and gtk_events_pending().
Creating new sources types
One of the unusual features of the GTK+ main loop functionality is that new
types of event source can be created and used in addition to the builtin type of
event source. A new event source type is used for handling GDK events. A new
source type is created by deriving from the GSource
structure. The derived type of source is represented by a structure that has the GSource structure as a first element, and other
elements specific to the new source type. To create an instance of the new
source type, call g_source_new() passing in the size of the derived
structure and a table of functions. These
GSourceFuncs
determine the behavior of the new source types.
New source types basically interact with with the main context in two ways.
Their prepare function in
GSourceFuncs
can set a timeout to determine the maximum amount of time that the main loop
will sleep before checking the source again. In addition, or as well, the source
can add file descriptors to the set that the main context checks using g_source_add_poll().
Customizing the main loop iteration
Single iterations of a
GMainContext
can be run with g_main_context_iteration(). In some cases, more
detailed control of exactly how the details of the main loop work is desired,
for instance, when integrating the GMainLoop
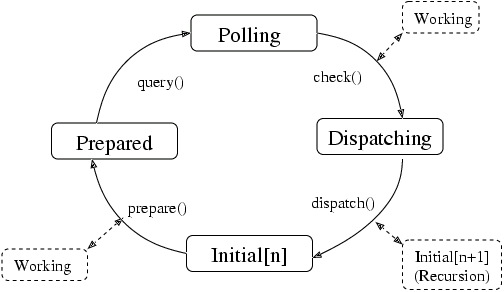
with an external main loop. In such cases, call the component functions of g_main_context_iteration() directly. These
functions are g_main_context_prepare(), g_main_context_query(), g_main_context_check() and g_main_context_dispatch().
The operation of these functions can best be seen in terms of a state diagram, as shown in Figure 1, “States of a Main Context”.
Details
GMainLoop
typedef struct _GMainLoop GMainLoop;
The GMainLoop struct is an opaque data type representing the main event loop of a GLib or GTK+ application.
g_main_loop_new ()
GMainLoop* g_main_loop_new GMainContext *context, gboolean is_running);
Creates a new GMainLoop structure.
context : |
a GMainContext (if
NULL, the
default context will be used). |
is_running : |
set to
TRUE to
indicate that the loop is running. This is not very important since
calling g_main_loop_run() will set this to TRUE anyway. |
| Returns : | a new GMainLoop. |
g_main_loop_ref ()
GMainLoop* g_main_loop_ref (GMainLoop *loop);
Increases the reference count on a GMainLoop object by one.
loop : |
a GMainLoop |
| Returns : | loop |
g_main_loop_unref ()
void g_main_loop_unref (GMainLoop *loop);
Decreases the reference count on a GMainLoop object by one. If the result is zero, free the loop and free all associated memory.
loop : |
a GMainLoop |
g_main_loop_run ()
void g_main_loop_run (GMainLoop *loop);
Runs a main loop until g_main_loop_quit() is called on the loop. If this
is called for the thread of the loop's
GMainContext, it will process events from the loop, otherwise it will
simply wait.
loop : |
a GMainLoop |
g_main_loop_quit ()
void g_main_loop_quit (GMainLoop *loop);
Stops a GMainLoop from running. Any calls to g_main_loop_run()
for the loop will return.
loop : |
a GMainLoop |
g_main_loop_is_running ()
gboolean g_main_loop_is_running (GMainLoop *loop);
Checks to see if the main loop is currently being run via g_main_loop_run().
loop : |
a GMainLoop. |
| Returns : | TRUE if the mainloop is currently being
run. |
g_main_loop_get_context ()
GMainContext* g_main_loop_get_context (GMainLoop *loop);
Returns the GMainContext of loop.
loop : |
a GMainLoop. |
| Returns : | the GMainContext of loop
|
g_main_new()
#define g_main_new(is_running)
Creates a new GMainLoop for the default main loop.
|
|
Warning: |
is_running : |
set to
TRUE to
indicate that the loop is running. This is not very important since
calling
g_main_run()
will set this to TRUE anyway. |
| Returns : | a new GMainLoop. |
g_main_destroy()
#define g_main_destroy(loop)
Frees the memory allocated for the GMainLoop.
|
|
Warning: |
loop : |
a GMainLoop. |
g_main_run()
#define g_main_run(loop)
Runs a main loop until it stops running.
|
|
Warning: |
loop : |
a GMainLoop. |
g_main_quit()
#define g_main_quit(loop)
Stops the GMainLoop. If
g_main_run()
was called to run the GMainLoop, it will now return.
|
|
Warning: |
loop : |
a GMainLoop. |
g_main_is_running()
#define g_main_is_running(loop)
Checks if the main loop is running.
|
|
Warning: |
loop : |
a GMainLoop. |
| Returns : | TRUE if the main loop is running. |
G_PRIORITY_HIGH
#define G_PRIORITY_HIGH -100
Use this for high priority event sources. It is not used within GLib or GTK+.
G_PRIORITY_DEFAULT
#define G_PRIORITY_DEFAULT 0
Use this for default priority event sources. In GLib this priority is used when
adding timeout functions with
g_timeout_add(). In GDK this priority is used for
events from the X server.
G_PRIORITY_HIGH_IDLE
#define G_PRIORITY_HIGH_IDLE 100
Use this for high priority idle functions. GTK+ uses G_PRIORITY_HIGH_IDLE + 10 for resizing operations, and G_PRIORITY_HIGH_IDLE + 20 for redrawing operations. (This is done to ensure that any pending resizes are processed before any pending redraws, so that widgets are not redrawn twice unnecessarily.)
G_PRIORITY_DEFAULT_IDLE
#define G_PRIORITY_DEFAULT_IDLE 200
Use this for default priority idle functions. In GLib this priority is used when
adding idle functions with
g_idle_add().
G_PRIORITY_LOW
#define G_PRIORITY_LOW 300
Use this for very low priority background tasks. It is not used within GLib or GTK+.
GMainContext
typedef struct _GMainContext GMainContext;
The GMainContext struct is an opaque data type representing a set of sources to be handled in a main loop.
g_main_context_new ()
GMainContext* g_main_context_new (void);
Creates a new GMainContext strcuture
| Returns : | the new GMainContext |
g_main_context_ref ()
GMainContext* g_main_context_ref (GMainContext *context);
Increases the reference count on a GMainContext object by one.
context : |
a GMainContext |
| Returns : | the context that was passed
in (since 2.6) |
g_main_context_unref ()
void g_main_context_unref (GMainContext *context);
Decreases the reference count on a GMainContext object by one. If the result is zero, free the context and free all associated memory.
context : |
a GMainContext |
g_main_context_default ()
GMainContext* g_main_context_default (void);
Returns the default main context. This is the main context used for main loop functions when a main loop is not explicitly specified.
| Returns : | the default main context. |
g_main_context_iteration ()
gboolean g_main_context_iteration (GMainContext *context, gboolean may_block);
Runs a single iteration for the given main loop. This involves checking to see
if any event sources are ready to be processed, then if no events sources are
ready and may_block
is TRUE,
waiting for a source to become ready, then dispatching the highest priority
events sources that are ready. Note that even when may_block is TRUE,
it is still possible for g_main_context_iteration() to return
FALSE,
since the the wait may be interrupted for other reasons than an event source
becoming ready.
context : |
a GMainContext (if
NULL, the
default context will be used) |
may_block : |
whether the call may block. |
| Returns : |
TRUE if events were dispatched. |
g_main_iteration()
#define g_main_iteration(may_block)
Runs a single iteration for the default GMainContext.
|
|
Warning: |
g_main_context_pending ()
gboolean g_main_context_pending (GMainContext *context);
Checks if any sources have pending events for the given context.
context : |
a GMainContext (if
NULL, the
default context will be used) |
| Returns : |
TRUE if events are pending. |
g_main_pending()
#define g_main_pending()
Checks if any events are pending for the default GMainContext (i.e. ready to be processed).
|
|
Warning: |
| Returns : | TRUE if any events are pending. |
g_main_context_find_source_by_id ()
GSource* g_main_context_find_source_by_id (GMainContext *context, guint source_id);
Finds a GSource given a pair of context and ID.
context : |
a GMainContext (if NULL, the
default context will be used) |
source_id : |
the source ID, as returned by g_source_get_id() |
| Returns : | the GSource if found, otherwise, NULL |
g_main_context_find_source_by_user_data ()
GSource* g_main_context_find_source_by_user_data (GMainContext *context, gpointer user_data);
Finds a source with the given user data for the callback. If multiple sources exist with the same user data, the first one found will be returned.
context : |
a GMainContext |
user_data : |
the user_data for the callback. |
| Returns : | the source, if one was found, otherwise
NULL |
g_main_context_find_source_by_funcs_user_data ()
GSource* g_main_context_find_source_by_funcs_user_data (GMainContext *context, GSourceFuncs *funcs, gpointer user_data);
Finds a source with the given source functions and user data. If multiple sources exist with the same source function and user data, the first one found will be returned.
context : |
a GMainContext (if NULL, the
default context will be used). |
funcs : |
the source_funcs
passed to g_source_new(). |
user_data : |
the user data from the callback. |
| Returns : | the source, if one was found, otherwise
NULL |
g_main_context_wakeup ()
void g_main_context_wakeup (GMainContext *context);
If context is currently waiting in a
poll(), interrupt the poll(), and continue
the iteration process.
context : |
a GMainContext |
g_main_context_acquire ()
gboolean g_main_context_acquire (GMainContext *context);
Tries to become the owner of the specified context. If some other context is the
owner of the context, returns FALSE immediately.
Ownership is properly recursive: the owner can require ownership again and will
release ownership when g_main_context_release()
is called as many times as g_main_context_acquire().
Ownership of a context is a pre-requisite before a call to g_main_context_prepare(), g_main_context_query(),
g_main_context_check(), g_main_context_dispatch().
context : |
a GMainContext |
| Returns : | TRUE if the operation succeeded, and
this thread is now the owner of context.
|
g_main_context_release ()
void g_main_context_release (GMainContext *context);
Releases ownership of a context previously acquired by this thread with g_main_context_acquire(). If the context was
acquired multiple times, the only release ownership when g_main_context_release()
is called as many times as it was acquired.
context : |
a GMainContext |
g_main_context_is_owner ()
gboolean g_main_context_is_owner (GMainContext *context);
Determines whether this thread holds the (recursive) ownership of this
GMaincontext. This is useful to know before waiting on another thread
that may be blocking to get ownership of context.
context : |
a GMainContext |
| Returns : | TRUE
if current thread is owner of context.
|
g_main_context_wait ()
gboolean g_main_context_wait (GMainContext *context, GCond *cond, GMutex *mutex);
Tries to become the owner of the specified context, as with g_main_context_acquire(). But if another thread is
the owner, atomically drop mutex
and wait on cond until that owner
releases ownership or until cond
is signaled, then try again (once) to become the owner.
context : |
a GMainContext |
cond : |
a condition variable |
mutex : |
a mutex, currently held |
| Returns : |
TRUE if the operation succeeded, and this thread is now the
owner of context.
|
g_main_context_prepare ()
gboolean g_main_context_prepare (GMainContext *context, gint *priority);
Prepares to poll sources within a main loop. The resulting information for
polling is determined by calling g_main_context_query().
context : |
a GMainContext |
priority : |
location to store priority of highest priority source already ready. |
| Returns : |
TRUE if some source is ready to be dispatched prior to
polling. |
g_main_context_query ()
gint g_main_context_query (GMainContext *context, gint max_priority, gint *timeout_, GPollFD *fds, gint n_fds);
Determines information necessary to poll this main loop.
context : |
a GMainContext |
max_priority : |
maximum priority source to check |
timeout_ : |
location to store timeout to be used in polling |
fds : |
location to store GPollFD records that need to be polled. |
n_fds : |
length of fds. |
| Returns : | the number of records actually stored in fds, or, if more than n_fds records need to be stored, the number
of records that need to be stored. |
g_main_context_check ()
gint g_main_context_check (GMainContext *context, gint max_priority, GPollFD *fds, gint n_fds);
Passes the results of polling back to the main loop.
context : |
a GMainContext |
max_priority : |
the maximum numerical priority of sources to check |
fds : |
array of GPollFD's that was passed to the last call to g_main_context_query() |
n_fds : |
return value of g_main_context_query() |
| Returns : |
TRUE if some sources are ready to be dispatched. |
g_main_context_dispatch ()
void g_main_context_dispatch (GMainContext *context);
Dispatches all pending sources.
context : |
a GMainContext |
g_main_context_set_poll_func ()
void g_main_context_set_poll_func (GMainContext *context, GPollFunc func);
Sets the function to use to handle polling of file descriptors. It will be used
instead of the poll()
system call (or GLib's replacement function, which is used where poll() isn't available).
This function could possibly be used to integrate the GLib event loop with an external event loop.
context : |
a GMainContext |
func : |
the function to call to poll all file descriptors |
g_main_context_get_poll_func ()
GPollFunc g_main_context_get_poll_func (GMainContext *context);
Gets the poll function set by g_main_context_set_poll_func().
context : |
a GMainContext |
| Returns : | the poll function |
GPollFunc ()
gint (*GPollFunc) (GPollFD *ufds, guint nfsd, gint timeout_);
Specifies the type of function passed to g_main_context_set_poll_func(). The semantics of
the function should match those of the
poll()
ufds : |
an array of GPollFD elements. |
nfsd : |
the number of elements in ufds.
|
timeout_ : |
the maximum time to wait for an event of the file descriptors. A negative value indicates an infinite timeout. |
| Returns : | the number of GPollFD elements which have events or errors reported, or -1 if an error occurred. |
g_main_context_add_poll ()
void g_main_context_add_poll (GMainContext *context, GPollFD *fd, gint priority);
Adds a file descriptor to the set of file descriptors polled for this context.
This will very seldomly be used directly. Instead a typical event source will
use g_source_add_poll() instead.
context : |
a GMainContext (or
NULL
for the default context) |
fd : |
a GPollFD structure holding information about a file descriptor to watch. |
priority : |
the priority for this file descriptor which should be the same as the
priority used for g_source_attach() to ensure that the file
descriptor is polled whenever the results may be needed. |
g_main_context_remove_poll ()
void g_main_context_remove_poll (GMainContext *context, GPollFD *fd);
Removes file descriptor from the set of file descriptors to be polled for a particular context.
context : |
a GMainContext |
fd : |
a GPollFD descriptor previously added with g_main_context_add_poll() |
g_main_depth ()
int g_main_depth (void);
Return value: The main loop recursion level in the current thread
| Returns : | the depth of the stack of calls to g_main_context_dispatch() on any
GMainContext
in the current thread. That is, when called from the toplevel, it gives
0. When called from within a callback from g_main_context_iteration()
(or g_main_loop_run(), etc.) it returns 1. When called
from within a callback to a recursive call to g_main_context_iterate(), it returns 2. And so forth.
This function is useful in a situation like the following: Imagine an
extremely simple "garbage collected" system.
Example 1. static GList *free_list; gpointer allocate_memory (gsize size) { gpointer result = g_malloc (size); free_list = g_list_prepend (free_list, result); return result; } void free_allocated_memory (void) { GList *l; for (l = free_list; l; l = l->next); g_free (l->data); g_list_free (free_list); free_list = NULL; } [...] while (TRUE); { g_main_context_iteration (NULL, TRUE);free_allocated_memory();
}
free_allocated_memory() does not work, since the idle function
could be called from a recursive callback. This can be fixed by using g_main_depth()
Example 2. gpointer allocate_memory (gsize size) { FreeListBlock *block = g_new (FreeListBlock, 1);\ block->mem = g_malloc (size); block->depth = g_main_depth(); free_list = g_list_prepend (free_list, block); return block->mem; } void free_allocated_memory (void) { GList *l; int depth = g_main_depth(); for (l = free_list; l; ); { GList *next = l->next; FreeListBlock *block = l->data; if (block->depth > depth) { g_free (block->mem); g_free (block); free_list = g_list_delete_link (free_list, l); } l = next; } }g_main_depth() to solve problems with re-entrancy.
For instance, while waiting for data to be received from the network in
response to a menu item, the menu item might be selected again. It might
seem that one could make the menu item's callback return immediately and
do nothing if g_main_depth() returns a value greater than 1.
However, this should be avoided since the user then sees selecting the
menu item do nothing. Furthermore, adding these checks all over the
code, since there are many things that the user could do. Instead, use
the following techniques:
|
g_main_set_poll_func()
#define g_main_set_poll_func(func)
|
|
Warning: |
Sets the function to use for the handle polling of file descriptors for the default main context.
func : |
the function to call to poll all file descriptors. |
g_timeout_source_new ()
GSource* g_timeout_source_new (guint interval);
Creates a new timeout source.
The source will not initially be associated with any
GMainContext
and must be added to one with g_source_attach() before it will be executed.
interval : |
the timeout interval in milliseconds. |
| Returns : | the newly-created timeout source |
g_timeout_add ()
guint g_timeout_add (guint interval, GSourceFunc function, gpointer data);
Sets a function to be called at regular intervals, with the default priority, G_PRIORITY_DEFAULT. The function is called repeatedly
until it returns FALSE, at which point the timeout
is automatically destroyed and the function will not be called again. The first
call to the function will be at the end of the first
interval.
Note that timeout functions may be delayed, due to the processing of other event sources. Thus they should not be relied on for precise timing. After each call to the timeout function, the time of the next timeout is recalculated based on the current time and the given interval (it does not try to 'catch up' time lost in delays).
interval : |
the time between calls to the function, in milliseconds (1/1000ths of a second) |
function : |
function to call |
data : |
data to pass to function
|
| Returns : | the ID (greater than 0) of the event source. |
g_timeout_add_full ()
guint g_timeout_add_full (gint priority, guint interval, GSourceFunc function, gpointer data, GDestroyNotify notify);
Sets a function to be called at regular intervals, with the given priority. The
function is called repeatedly until it returns
FALSE, at which point the timeout is automatically
destroyed and the function will not be called again. The
notify
function is called when the timeout is destroyed. The first call to the function
will be at the end of the first interval.
Note that timeout functions may be delayed, due to the processing of other event sources. Thus they should not be relied on for precise timing. After each call to the timeout function, the time of the next timeout is recalculated based on the current time and the given interval (it does not try to 'catch up' time lost in delays).
priority : |
the priority of the idle source. Typically this will be in the range between G_PRIORITY_DEFAULT_IDLE and G_PRIORITY_HIGH_IDLE. |
interval : |
the time between calls to the function, in milliseconds (1/1000ths of a second) |
function : |
function to call |
data : |
data to pass to function
|
notify : |
function to call when the idle is removed, or NULL |
| Returns : | the ID (greater than 0) of the event source. |
g_idle_source_new ()
GSource* g_idle_source_new (void);
Creates a new idle source.
The source will not initially be associated with any
GMainContext
and must be added to one with g_source_attach() before it will be executed. Note
that the default priority for idle sources is
G_PRIORITY_DEFAULT_IDLE, as compared to other
sources which have a default priority of
G_PRIORITY_DEFAULT.
| Returns : | the newly-created idle source |
g_idle_add ()
guint g_idle_add (GSourceFunc function, gpointer data);
Adds a function to be called whenever there are no higher priority events
pending to the default main loop. The function is given the default idle
priority, G_PRIORITY_DEFAULT_IDLE. If the function returns
FALSE it is automatically removed from the list of event sources and will
not be called again.
function : |
function to call |
data : |
data to pass to function.
|
| Returns : | the ID (greater than 0) of the event source. |
g_idle_add_full ()
guint g_idle_add_full (gint priority, GSourceFunc function, gpointer data, GDestroyNotify notify);
Adds a function to be called whenever there are no higher priority events
pending. If the function returns FALSE
it is automatically removed from the list of event sources and will not be
called again.
priority : |
the priority of the idle source. Typically this will be in the range btweeen G_PRIORITY_DEFAULT_IDLE and G_PRIORITY_HIGH_IDLE. |
function : |
function to call |
data : |
data to pass to function
|
notify : |
function to call when the idle is removed, or NULL |
| Returns : | the ID (greater than 0) of the event source. |
g_idle_remove_by_data ()
gboolean g_idle_remove_by_data (gpointer data);
Removes the idle function with the given data.
data : |
the data for the idle source's callback. |
| Returns : | TRUE if an idle source was found and
removed. |
GPid
typedef int GPid;
A type which is used to hold a process identification. On Unix, processes are identified by a process id (an integer), while Windows uses process handles (which are pointers).
GChildWatchFunc ()
void (*GChildWatchFunc) (GPid pid, gint status, gpointer data);
The type of functions to be called when a child exists.
pid : |
the process id of the child process |
status : |
Status information about the child process, see waitpid(2) for more information about this field |
data : |
user data passed to g_child_watch_add() |
g_child_watch_source_new ()
GSource* g_child_watch_source_new (GPid pid);
Creates a new child_watch source.
The source will not initially be associated with any
GMainContext
and must be added to one with g_source_attach() before it will be executed.
Note that child watch sources can only be used in conjunction with g_spawn... when the
G_SPAWN_DO_NOT_REAP_CHILD
flag is used.
Note that on platforms where GPid
must be explicitely closed (see g_spawn_close_pid())
pid
must not be closed while the source is still active. Typically, a want to
call
g_spawn_close_pid() in the callback function for
the source.
Note further that using g_child_watch_source_new() is not compatible with
calling waitpid(-1) in the application. Calling
waitpid() for individual pids will still work fine.
pid : |
process id of a child process to watch. On Windows, a HANDLE for the process to watch (which actually doesn't have to be a child). |
| Returns : | the newly-created child watch source |
g_child_watch_add ()
guint g_child_watch_add (GPid pid, GChildWatchFunc function, gpointer data);
Sets a function to be called when the child indicated by pid exits, at a default priority, G_PRIORITY_DEFAULT.
Note that on platforms where GPid
must be explicitely closed (see g_spawn_close_pid())
pid
must not be closed while the source is still active. Typically, a want to call
g_spawn_close_pid() in the callback function for
the source.
GLib supports only a single callback per process id.
pid : |
process id of a child process to watch |
function : |
function to call |
data : |
data to pass to function
|
| Returns : | the ID (greater than 0) of the event source. |
g_child_watch_add_full ()
guint g_child_watch_add_full (gint priority, GPid pid, GChildWatchFunc function, gpointer data, GDestroyNotify notify);
Sets a function to be called when the child indicated by pid exits, at a default priority, G_PRIORITY_DEFAULT.
Note that on platforms where GPid
must be explicitely closed (see g_spawn_close_pid())
pid
must not be closed while the source is still active. Typically, a want to call
g_spawn_close_pid() in the callback function for
the source.
GLib supports only a single callback per process id.
priority : |
the priority of the idle source. Typically this will be in the range between G_PRIORITY_DEFAULT_IDLE and G_PRIORITY_HIGH_IDLE. |
pid : |
process id of a child process to watch |
function : |
function to call |
data : |
data to pass to function
|
notify : |
function to call when the idle is removed, or NULL |
| Returns : | the ID (greater than 0) of the event source. |
GPollFD
typedef struct {
gint fd;
gushort events;
gushort revents;
} GPollFD;
| gint fd; | the file descriptor to poll (or a HANDLE on Win32 platforms). |
| gushort events; | a bitwise combination of flags from GIOCondition,
specifying which events should be polled for. Typically for reading from
a file descriptor use
G_IO_IN | G_IO_HUP |
G_IO_ERR, and for
writing use
G_IO_OUT |
G_IO_ERR. |
| gushort revents; | a bitwise combination of flags from GIOCondition,
returned from the |
GSource
typedef struct {
} GSource;
The GSource struct is an opaque data type representing an event source.
GSourceDummyMarshal ()
void (*GSourceDummyMarshal) (void);
This is just a placeholder for GClosureMarshal, which cannot be used here for dependency reasons.
GSourceFuncs
typedef struct {
gboolean (*prepare) (GSource *source, gint *timeout_);
gboolean (*check) (GSource *source);
gboolean (*dispatch) (GSource *source, GSourceFunc callback, gpointer user_data);
void (*finalize) (GSource *source); /* Can be NULL */
/* For use by g_source_set_closure */
GSourceFunc closure_callback;
GSourceDummyMarshal closure_marshal; /* Really is of type GClosureMarshal */
} GSourceFuncs;
The GSourceFuncs struct contains a table of functions used to handle event sources in a generic manner.
| prepare | Called before all the file descriptors are polled. If the source can
determine that it is ready here (without waiting for the results of the TRUE. It can also
return a timeout_
value which should be the maximum timeout (in milliseconds) which should
be passed to the
timeout_
values returned which were >= 0. |
| check | Called after all the file descriptors are polled. The source should
return TRUE if it is ready to be
dispatched. Note that some time may have passed since the previous
prepare function was called, so the source should be checked again here. |
| dispatch | Called to dispatch the event source, after it has returned TRUE in either its prepare
or its check function. The dispatch function is passed in a callback
function and data. The callback function may be NULL if the source was never connected to a callback
using g_source_set_callback(). The dispatch function should call the callback
function with user_data
and whatever additional parameters are needed for this type of event
source. |
| finalize | Called when the source is finalized. |
For idle sources, the prepare and check functions always return TRUE to indicate that the source is always ready to be
processed. The prepare function also returns a timeout value of 0 to ensure that
the
poll()
For timeout sources, the prepare and check functions both return TRUE if the timeout interval has expired. The prepare
function also returns a timeout value to ensure that the poll()
For file descriptor sources, the prepare function typically returns FALSE, since it must wait until
poll()
poll()poll()TRUE if so.
GSourceCallbackFuncs
typedef struct {
void (*ref) (gpointer cb_data);
void (*unref) (gpointer cb_data);
void (*get) (gpointer cb_data, GSource *source, GSourceFunc *func, gpointer *data);
} GSourceCallbackFuncs;
The GSourceCallbackFuncs struct contains functions for managing callback objects.
ref () |
Called when a reference is added to the callback object. |
unref () |
Called when a reference to the callback object is dropped. |
get () |
Called to extract the callback function and data from the callback object. |
g_source_new ()
GSource* g_source_new (GSourceFuncs *source_funcs, guint struct_size);
Creates a new GSource structure. The size is specified to allow
creating structures derived from GSource
that contain additional data. The size passed in must be at least
sizeof (GSource).
The source will not initially be associated with any
GMainContext
and must be added to one with g_source_attach() before it will be executed.
g_source_ref ()
GSource* g_source_ref (GSource *source);
Increases the reference count on a source by one.
source : |
a GSource |
| Returns : | source |
g_source_unref ()
void g_source_unref (GSource *source);
Decreases the reference count of a source by one. If the resulting reference count is zero the source and associated memory will be destroyed.
source : |
a GSource |
g_source_attach ()
guint g_source_attach (GSource *source, GMainContext *context);
Adds a GSource to a context
so that it will be executed within that context.
source : |
a GSource |
context : |
a GMainContext (if
NULL, the
default context will be used) |
| Returns : | the ID (greater than 0) for the source within the GMainContext |
g_source_destroy ()
void g_source_destroy (GSource *source);
Removes a source from its GMainContext, if any, and mark it as destroyed. The source cannot be subsequently added to another context.
source : |
a GSource |
g_source_set_priority ()
void g_source_set_priority (GSource *source, gint priority);
Sets the priority of a source. While the main loop is being run, a source will be dispatched if it is ready to be dispatched and no sources at a higher (numerically smaller) priority are ready to be dispatched.
source : |
a GSource |
priority : |
the new priority. |
g_source_get_priority ()
gint g_source_get_priority (GSource *source);
Gets the priority of a source.
source : |
a GSource |
| Returns : | the priority of the source |
g_source_set_can_recurse ()
void g_source_set_can_recurse (GSource *source, gboolean can_recurse);
Sets whether a source can be called recursively. If can_recurse is
TRUE,
then while the source is being dispatched then this source will be processed
normally. Otherwise, all processing of this source is blocked until the dispatch
function returns.
source : |
a GSource |
can_recurse : |
whether recursion is allowed for this source |
g_source_get_can_recurse ()
gboolean g_source_get_can_recurse (GSource *source);
Checks whether a source is allowed to be called recursively. see g_source_set_can_recurse().
source : |
a GSource |
| Returns : | whether recursion is allowed. |
g_source_get_id ()
guint g_source_get_id (GSource *source);
Returns the numeric ID for a particular source. The ID of a source is a positive
integer which is unique within a particular main loop context. The reverse
mapping from ID to source is done by g_main_context_find_source_by_id().
source : |
a GSource |
| Returns : | the ID (greater than 0) for the source |
g_source_get_context ()
GMainContext* g_source_get_context (GSource *source);
Gets the GMainContext with which the source is associated. Calling this function on a destroyed source is an error.
source : |
a GSource |
| Returns : | the GMainContext with which the source is associated, or
NULL if the context has not yet been added to a source. |
g_source_set_callback ()
void g_source_set_callback (GSource *source, GSourceFunc func, gpointer data, GDestroyNotify notify);
Sets the callback function for a source. The callback for a source is called from the source's dispatch function.
The exact type of func depends on the
type of source; ie. do not count on func
being called with data as its first
parameter.
Typically, do not use this function. Instead use functions specific to the type of source being used.
source : |
the source |
func : |
a callback function |
data : |
the data to pass to callback function |
notify : |
a function to call when data
is no longer in use, or NULL. |
GSourceFunc ()
gboolean (*GSourceFunc) (gpointer data);
Specifies the type of function passed to g_timeout_add(), g_timeout_add_full(),
g_idle_add(), and g_idle_add_full().
data : |
data passed to the function, set when the source was created with one of the above functions. |
| Returns : | it should return
FALSE if the
source should be removed. |
g_source_set_callback_indirect ()
void g_source_set_callback_indirect (GSource *source, gpointer callback_data, GSourceCallbackFuncs *callback_funcs);
Sets the callback function storing the data as a refcounted callback "object".
This is used internally. Note that calling g_source_set_callback_indirect() assumes an initial
reference count on callback_data, and
thus
callback_funcs->unref will eventually be
called once more than callback_funcs->ref.
source : |
the source |
callback_data : |
pointer to callback data "object" |
callback_funcs : |
functions for reference counting
callback_data
and getting the callback and data |
g_source_add_poll ()
void g_source_add_poll (GSource *source, GPollFD *fd);
Adds a file descriptor to the set of file descriptors polled for this source.
This is usually combined with g_source_new() to add an event source. The event
source's check function will typically test the
revents field in the GPollFD
struct and return TRUE if events need to be
processed.
g_source_remove_poll ()
void g_source_remove_poll (GSource *source, GPollFD *fd);
Removes a file descriptor from the set of file descriptors polled for this source.
source : |
a GSource |
fd : |
a GPollFD structure previously passed to g_source_add_poll(). |
g_source_get_current_time ()
void g_source_get_current_time (GSource *source, GTimeVal *timeval);
Gets the "current time" to be used when checking this source. The advantage of
calling this function over calling g_get_current_time() directly is that when checking
multiple sources, GLib can cache a single value instead of having to repeatedly
get the system time.
g_source_remove ()
gboolean g_source_remove (guint tag);
Removes the source with the given id from the default main context. The id of a
GSource
is given by g_source_get_id(), or will be returned by the
functions g_source_attach(),
g_idle_add(),
g_idle_add_full(),
g_timeout_add(), g_timeout_add_full(), g_child_watch_add(),
g_child_watch_add_full(),
g_io_add_watch(), and g_io_add_watch_full().
See also g_source_destroy().
tag : |
the id of the source to remove. |
| Returns : |
TRUE if the source was found and removed. |
g_source_remove_by_funcs_user_data ()
gboolean g_source_remove_by_funcs_user_data (GSourceFuncs *funcs, gpointer user_data);
Removes a source from the default main loop context given the source functions and user data. If multiple sources exist with the same source functions and user data, only one will be destroyed.
funcs : |
The source_funcs
passed to g_source_new() |
user_data : |
the user data for the callback |
| Returns : |
TRUE if a source was found and removed. |
|
© 2008-2009 Nokia Corporation. All rights reserved. This documentation can be used in the connection with this Product to help and support the user. |
|