Overview
The SIP Client API manages the multimedia sessions, subscribes to events, and sends SIP messages. It also provides access to the basic services of the SIP stack such as:
Sending and receiving of SIP messages
Creating registrations
Forming and tearing down dialogs initiated by INVITE, REFER and SUBSCRIBE requests
Architectural relationships
The SIP Client API uses the client-server mechanism to interact with the SIP stack. This means more than one client can use the SIP stack at the same time. The calls to the SIP Client API are synchronous. The SIP Client API implements a set of callback functions to pass the events back to the application.
Capability information
The following table describes the capabilities required to use the SIP Client API and the conditions in which they are required:
| Capability | Reason needed |
|---|---|
NetworkServices |
to send or receive SIP messages |
WriteDeviceData |
to create an instance of the |
NetworkControl Location ReadDeviceData |
to use the function |
Extending the API
SIP Client API cannot be extended.
SIP Client API class structure
CSIP, MSIPObserver, CSIPConnection and MSIPConnectionObserver
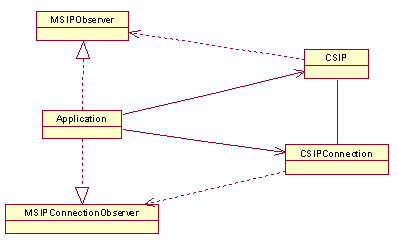
An application creates a single instance of the CSIP class,
and implements the callback functions defined by MSIPObserver.
The CSIP uses the MSIPObserver functions.
The CSIP class asks the supported security mechanisms and
determines whether a CSIPConnection object exists for a
given IAP.
The CSIP object creates an instance
of CSIPConnection that allows you to send standalone SIP
requests and ask for the state of the network connection. Responses are received
through the MSIPConnectionObserver interface that defines
a set of callback functions that an application must implement.
An
application can have many CSIPConnection objects, but each
of them must have a different IAP.
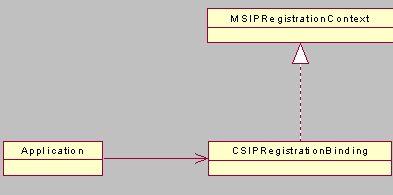
An existing CSIPConnection is required to create
an instance of CSIPRegistrationBinding. The CSIPRegistrationBinding class
provides services for registration, updating the registration, and deregistration.
This class also provides instructions to the SIP stack to automatically refresh
the registration, and to query and set the outbound proxy used by the registration.
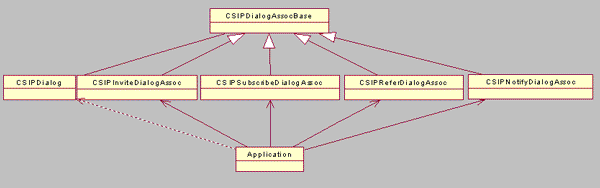
CSIPDialogAssocBase is the base class for SIP
dialog associations, such as CSIPInviteDialogAssoc, CSIPSubscribeDialogAssoc, CSIPReferDialogAssoc and CSIPNotifyDialogAssoc. The CSIPDialogAssocBase class
is used to obtain the associated SIP dialog, for the associated CSIPDialog instance,
and for sending a non-target Refresh request within the dialog.
Note: The
SIP Client API creates the CSIPDialog instance, it cannot
be created by the application.
If any of the CSIPInviteDialogAssoc, CSIPSubscribeDialogAssoc, CSIPReferDialogAssoc and CSIPNotifyDialogAssoc objects
are associated, they are bound to an existing CSIPDialog object,
or they can be used to create a new CSIPDialog object.
Note:
CSIPInviteDialogAssocallows an application to initiate a dialog and to sendINVITE,,PRACK,,ACK,UPDATE,andBYErequests related to the dialog.CSIPSubscribeDialogAssocallows an application to subscribe to different events by sending SUBSCRIBE and UNSUBSCRIBE requests. It also orders the SIP stack to automatically refresh the SUBSCRIBE request.CSIPReferDialogAssocallows an application to define and send REFER requests.CSIPNotifyDialogAssocallows an application to define and send NOTIFY requests.
Sent and received network requests
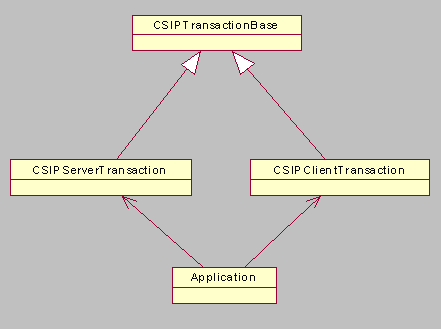
When a SIP request is sent to the network, the SIP Client API implementation
creates a CSIPClientTransaction object and returns it to
the application. A CSIPClientTransaction object represents
the SIP transaction and consists of the SIP request and the SIP response.
After receiving a response, the application gets CSIPResponseElements from
the CSIPClientTransaction object. Note: Some client
transactions can also be cancelled or refreshed.
When a SIP request
is received from the network, it is passed to the application as a CSIPServerTransaction object.
The application gets CSIPRequestElements from the CSIPServerTransaction object.
A CSIPRequestElements object describes the kind of SIP request
received. After the application determines the type of response to send, it
uses the CSIPServerTransaction to send the responses.
CSIPTransactionBase is
the base class for CSIPClientTransaction and CSIPServerTransaction.
It provides the functions to obtain the current state of the transaction and
the transaction type. Some operations are only allowed when the transaction
is in a certain state. Note: The SIP Client API creates instances of CSIPClientTransaction and CSIPServerTransaction and they cannot be created by the application.
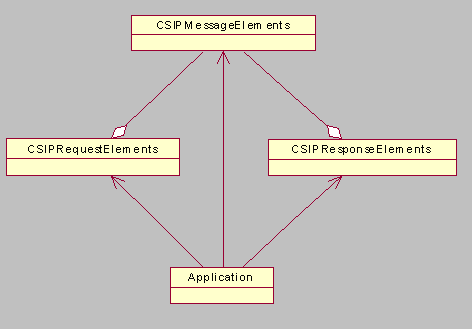
When a SIP request is sent to the network, the SIP Client API implementation
creates a CSIPClientTransaction object and returns it to
the application. A CSIPClientTransaction object represents
the SIP transaction and consists of the SIP request and the SIP response.
After receiving a response the application gets CSIPResponseElements from
the CSIPClientTransaction object. Note: Some client
transactions can be cancelled or refreshed.
When a SIP request is
received from the network, it is passed to the application as a CSIPServerTransaction object.
The application gets CSIPRequestElements from the CSIPServerTransaction object.
A CSIPRequestElements object describes the type of SIP request
received. After the application determines the type of response to send, it
uses the CSIPServerTransaction to send the responses.
CSIPTransactionBase is
the base class for CSIPClientTransaction and CSIPServerTransaction.
It provides functions to obtain the current state of the transaction and the
transaction type. Some operations are only allowed when the transaction is
in a certain state. Note: The SIP Client API creates instances of CSIPClientTransaction and CSIPServerTransaction and they cannot be created by the application.
Automatically refreshing a SIP request
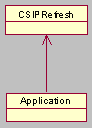
The SIP stack automatically refreshes a SIP request using the CSIPRefresh object. REGISTER, SUBSCRIBE and a request outside the dialog are refreshed. After
sending a refresh request, the application queries the state of the refresh
from CSIPRefresh.
CSIPRefresh provides
functions for updating and terminating the refresh, for requests outside the
dialog. The CSIPRegistrationBinding and CSIPSubscribeDialogAssoc classes
are used to update and terminate a refreshed REGISTER or SUBSCRIBE.
Managing HTTP digest security settings

An application must create an instance of the CSIP class
to use CSIPHttpDigest. The CSIPHttpDigest class
manages HTTP digest security settings and contains only static functions.
Memory used
After
the CSIP and CSIPConnection objects
are created, most of the memory consumed is by CSIPMessageElements, CSIPRequestElements and CSIPResponseElements classes. CSIPTransactionBase holds the most recent SIP
response in a CSIPResponseElements object. When another
response is received, the previous CSIPResponseElements object
is deleted and a new one is created.
CSIPClientTransaction contains
a CSIPRequestElements object until the SIP request is transferred
to the server side of the SIP stack. CSIPServerTransaction contains
the SIP request as CSIPRequestElements. The application
owns the CSIPClientTransaction and CSIPServerTransaction objects.
When the transaction terminates, the application deletes these objects to
conserve memory.
A non-INVITE CSIPClientTransaction is
deleted when it has received a final response or when the ErrorOccured() callback
is called. A non-INVITE CSIPServerTransaction is
deleted after the application sends a final response.
The INVITE related
transactions are deleted if the ErrorOccured() callback function
is called. These transactions behave differently because of the presence of
an ACK.
When the application sends a 2xx response
to an INVITE related CSIPServerTransaction,
it enters the CSIPTransactionBase::ETerminated state and
it is deleted at this point. A new CSIPServerTransaction object
receives the ACK.
When the application sends an INVITE request
and the CSIPClientTransaction receives a 2xx response, the
transaction enters the CSIPTransactionBase::ETerminated state.
The associated CSIPClientTransaction must not be deleted
as it is required to send the ACK and also to receive the MSIPConnectionObserver::InviteCompleted() callback.
An INVITE related CSIPClientTransaction must
be deleted only after a MSIPConnectionObserver::InviteCompleted or MSIPConnectionObserver
::ErrorOccured event is received, or if the state of the associated CSIPConnection goes
to CSIPConnection::EInactive or CSIPConnection::EUnavailable.