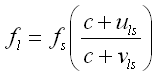
|
JSR-234 1.1 | |||||||
| PREV CLASS NEXT CLASS | FRAMES NO FRAMES | |||||||
| SUMMARY: NESTED | FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | DETAIL: FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | |||||||
public interface DopplerControl
DopplerControl is an interface for manipulating the settings of an effect called
Doppler. It can be obtained either for the Spectator (in which case
it specifies the listener's velocity) or a SoundSource3D (in which cases it specifies a
sound source's velocity). The DopplerControl must be enabled before it has any effect.
Please see the section below on
Synthesizing Doppler with PitchControl
if DopplerControl is not supported.
Doppler is the change in frequency perceived by a listener in the sound emitted from a sound source when the distance between them is rapidly increasing or decreasing. The frequency shift is defined by the following formula:
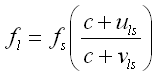
where:
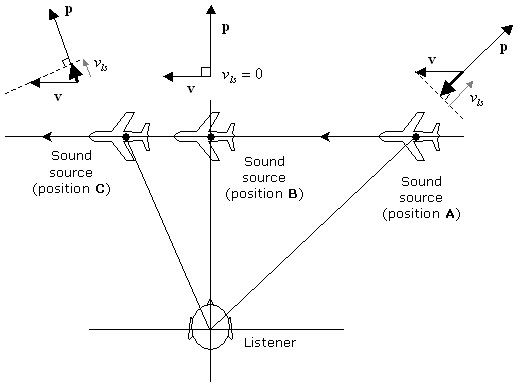
The following diagram illustrates how vls changes during a simple scenario in which the listener is stationary (uls = 0) while a sound source (whose position relative to the listener at any point in time is denoted by the vector p) flies by at a constant velocity v:
The application need only specify the absolute velocity of the Spectator
and each SoundSource3D via the
setVelocityCartesian or
setVelocitySpherical method of each of their DopplerControls.
There is normally no need to calculate the Doppler frequency shift, because it is
calculated automatically by the implementation when the DopplerControl is enabled.
The velocity specified using these methods is used for Doppler purposes only and does not actually move the object. This allows a decoupling between position and velocity information, which can be useful in variable frame rate applications or when the CPU resources are low, to allow the actual positions of the objects to "catch up" with their theoretically projected positions while preserving their theoretical velocity, giving a continuous frequency shift curve. This is also useful in server-controlled or peer-to-peer applications such as multi-player games where sometimes only limited information is available about the other objects in the system.
NOTE: Specifying speeds in excess of 50 m/s may give unexpected results, as implementations may use an approximation to the Doppler formula which gives inaccurate answers at these high velocities.
The default values for the properties of all Doppler controls (whether the application has obtained them or not) are:
velocity = 0
enabled = false
DopplerControl from Spectator is an exception. It has
enabled = true
If the implementation does not support DopplerControl but does support
javax.microedition.media.control.PitchControl
for the content type being played, the application can use the following formula to manually
calculate the Doppler pitch shift PDoppler (in millisemitones) in a form suitable to
pass as the argument to
PitchControl.setPitch:
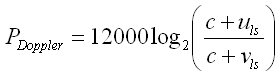
where:
In this way, the Doppler effect can be approximated with the PitchControl.
The next section describes how uls and vls may be calculated.
Let p be the position of the sound source relative to the position of the listener, defined in terms of the source's position ps and the listener's position pl:
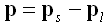
If u is the velocity of the listener in the medium, then uls (the speed of the listener in the direction from listener to sound source) can be calculated as follows:
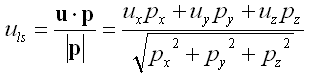
Similarly, if v is the velocity of the sound source in the medium, then vls (the speed of the sound source in the direction from listener to sound source) can be calculated as follows:
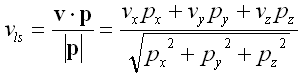
LocationControl,
PitchControl| Method Summary | |
|---|---|
int[] |
getVelocityCartesian()
Returns the current velocity, used in calculations for the Doppler effect. |
boolean |
isEnabled()
Returns whether this Doppler effect is currently active. |
void |
setEnabled(boolean dopplerEnabled)
Specifies if this Doppler effect is active or ignored. |
void |
setVelocityCartesian(int x,
int y,
int z)
Sets the velocity, used in calculations for the Doppler effect. |
void |
setVelocitySpherical(int azimuth,
int elevation,
int radius)
Sets the velocity, used in calculations for the Doppler effect. |
| Method Detail |
|---|
void setEnabled(boolean dopplerEnabled)
Specifies if this Doppler effect is active or ignored.
If the DopplerControl was fetched from the
Spectator, this method has no effect.
dopplerEnabled - a boolean specifying if this Doppler effect is to be appliedboolean isEnabled()
Returns whether this Doppler effect is currently active.
If the DopplerControl was fetched from the
Spectator, this method always returns true.
true if Doppler is being applied
void setVelocityCartesian(int x,
int y,
int z)
Sets the velocity, used in calculations for the Doppler effect.
The velocity is specified using right-handed cartesian components in millimeters per second (mm/s).
x - the x component of the new velocity in mm/sy - the y component of the new velocity in mm/sz - the z component of the new velocity in mm/ssetVelocitySpherical(int, int, int)int[] getVelocityCartesian()
Returns the current velocity, used in calculations for the Doppler effect.
The velocity is specified using right-handed cartesian components in millimeters per second (mm/s).
int array containing the x, y and z components of
the current velocity in mm/ssetVelocityCartesian(int, int, int)
void setVelocitySpherical(int azimuth,
int elevation,
int radius)
Sets the velocity, used in calculations for the Doppler effect.
The velocity is specified using spherical components. The radius component is
specified millimeters per second (mm/s).
azimuth - the azimuth angle of the new velocity in degrees.
The azimuth is measured from the negative z-axis in the direction of the x-axis.elevation - the elevation angle of the new velocity in degrees.
The elevation is measured from the x-z-plane in the direction of the y-axis.radius - the magnitude of the new velocity (namely the speed) in mm/ssetVelocityCartesian(int, int, int)
|
JSR-234 1.1 | |||||||
| PREV CLASS NEXT CLASS | FRAMES NO FRAMES | |||||||
| SUMMARY: NESTED | FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | DETAIL: FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | |||||||